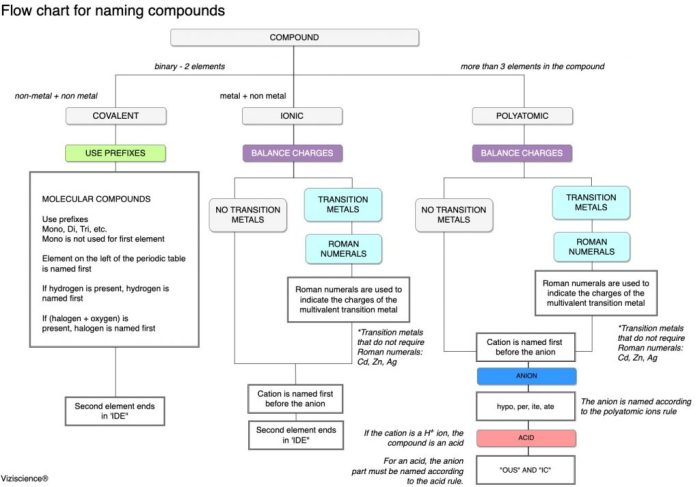
Embark on a journey through the realm of chemistry with our flowchart for naming ionic compounds, a visual guide that demystifies the intricacies of this fundamental aspect of chemical nomenclature. Prepare to navigate the intricacies of cation and anion naming conventions with ease, unraveling the secrets behind the formation of binary and polyatomic ionic compounds.
Our flowchart empowers you to decipher the language of ionic compounds, enabling you to confidently identify and name these essential chemical entities. Delve into the rules governing cation and anion nomenclature, understanding the significance of Roman numerals and variable charge.
Discover the nuances of naming polyatomic ions, unraveling the mysteries behind prefixes and suffixes.
Flowchart for Naming Ionic Compounds
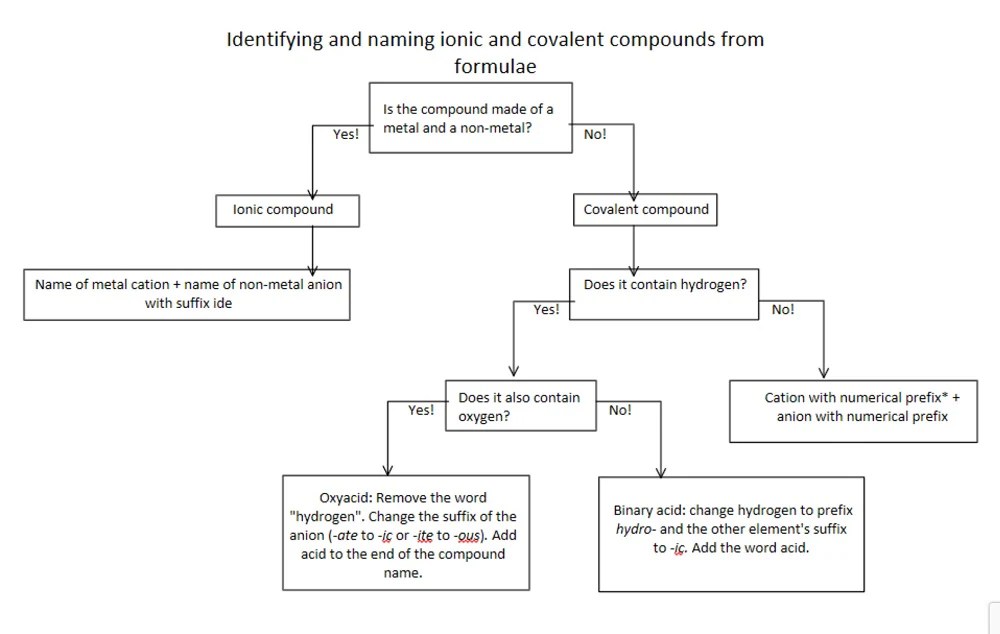
Ionic compounds are formed when a metal loses one or more electrons to a nonmetal. The resulting ions have opposite charges and are attracted to each other by electrostatic forces. The flowchart below Artikels the steps involved in naming ionic compounds.

Rules for Naming Cations
Cations are positively charged ions. They are named by the name of the metal followed by the suffix -ium. For example, Na+ is sodium ion, Ca2+ is calcium ion, and Al3+ is aluminum ion.
Some metals have variable charges. In these cases, the charge of the cation is indicated by a Roman numeral in parentheses after the name of the metal. For example, Fe2+ is iron(II) ion and Fe3+ is iron(III) ion.
Rules for Naming Anions
Anions are negatively charged ions. They are named by the root of the nonmetal name followed by the suffix -ide. For example, Cl- is chloride ion, O2- is oxide ion, and S2- is sulfide ion.
Some nonmetals have variable charges. In these cases, the charge of the anion is indicated by a prefix before the name of the nonmetal. The prefixes mono-, di-, tri-, tetra-, penta-, hexa-, and so on indicate charges of -1, -2, -3, -4, -5, and -6, respectively.
For example, NO2- is nitrite ion and NO3- is nitrate ion.
Naming Binary Ionic Compounds
Binary ionic compounds are compounds that contain only two elements, a metal and a nonmetal. To name a binary ionic compound, first name the cation followed by the anion. For example, NaCl is sodium chloride, CaO is calcium oxide, and Al2S3 is aluminum sulfide.
Naming Polyatomic Ions
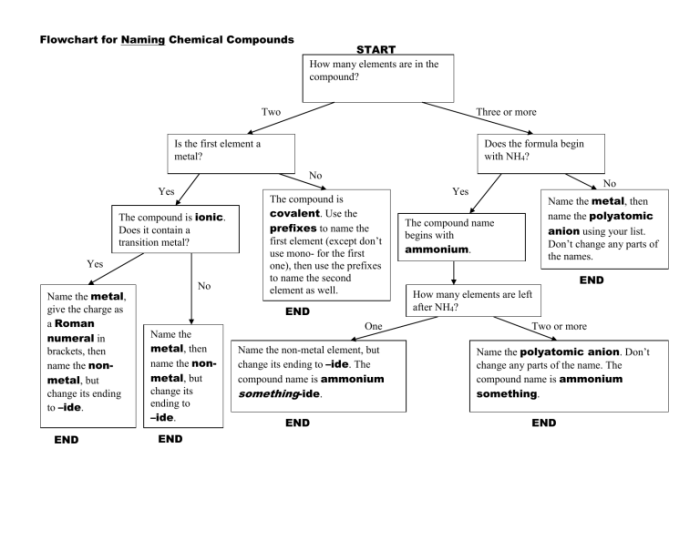
Polyatomic ions are ions that contain more than one atom. They are named by the root of the nonmetal name followed by the suffix -ate or -ite. The suffix -ate indicates a higher charge than the suffix -ite. For example, SO42- is sulfate ion and SO32- is sulfite ion.
Some polyatomic ions have variable charges. In these cases, the charge of the polyatomic ion is indicated by a prefix before the name of the polyatomic ion. The prefixes mono-, di-, tri-, tetra-, penta-, hexa-, and so on indicate charges of -1, -2, -3, -4, -5, and -6, respectively.
For example, HCO3- is bicarbonate ion and CO32- is carbonate ion.
Naming Ionic Compounds with Polyatomic Ions
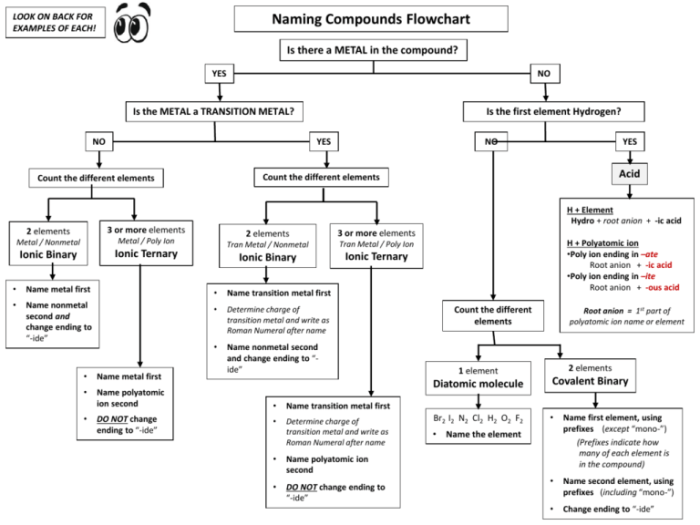
To name an ionic compound that contains a polyatomic ion, first name the cation followed by the polyatomic ion. For example, NaHCO3 is sodium bicarbonate and CaCO3 is calcium carbonate.
Practice Exercises
- Name the following ionic compounds:
- NaCl
- CaO
- Al2S3
- NaHCO3
- CaCO3
- Write the chemical formulas for the following ionic compounds:
- Sodium chloride
- Calcium oxide
- Aluminum sulfide
- Sodium bicarbonate
- Calcium carbonate
Helpful Answers
What is the purpose of a flowchart for naming ionic compounds?
A flowchart for naming ionic compounds provides a step-by-step visual guide to help you systematically name these compounds using established conventions.
How do I use the flowchart?
Follow the flowchart’s branches and boxes, applying the rules and guidelines for naming cations and anions to determine the correct name for the ionic compound.
What are the benefits of using a flowchart for naming ionic compounds?
The flowchart simplifies the naming process, minimizes errors, and enhances your understanding of ionic compound nomenclature.