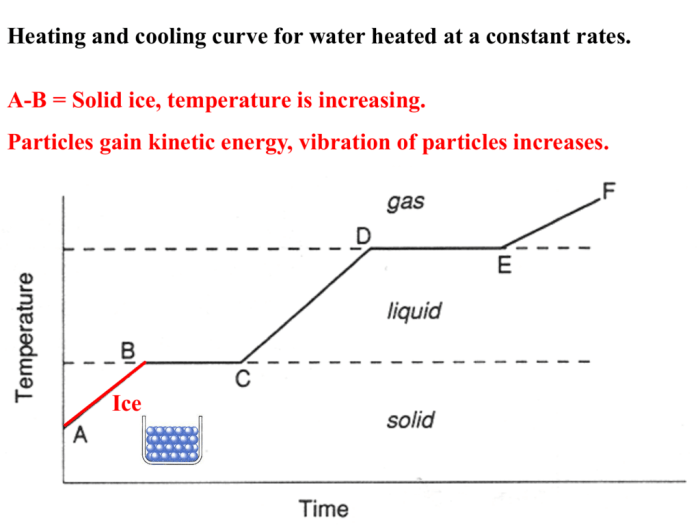
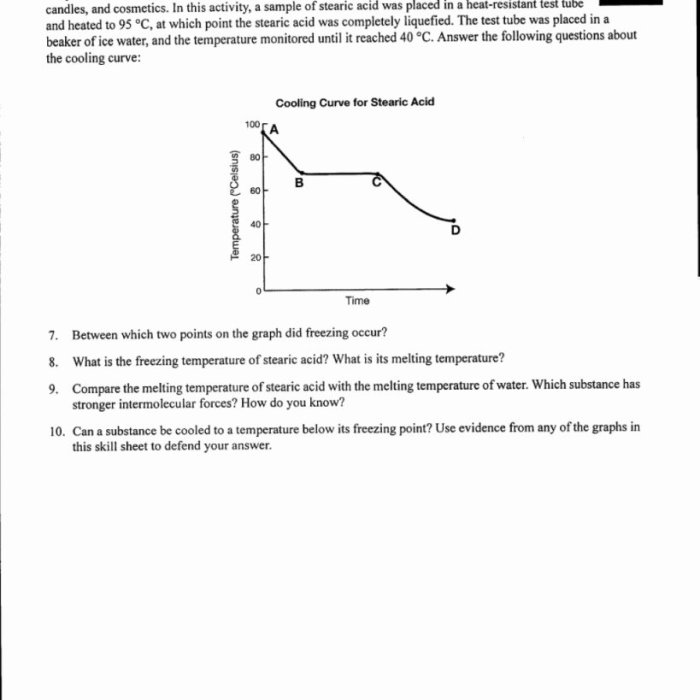
Heating and cooling curves worksheet answers provide valuable insights into the thermal properties of substances. These curves illustrate the changes in temperature as a substance undergoes heating or cooling processes, revealing crucial information about its physical and chemical behavior.
This guide delves into the concepts, procedures, and applications of heating and cooling curves, empowering you with the knowledge to analyze and interpret these curves effectively.
Heating and Cooling Curves: Heating And Cooling Curves Worksheet Answers
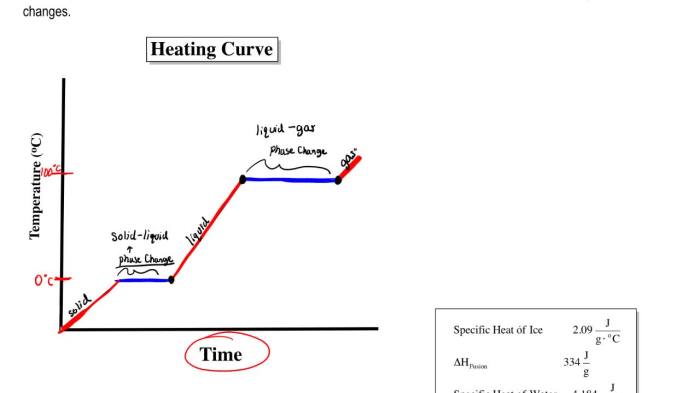
Heating and cooling curves are graphical representations of the temperature change of a substance as it undergoes heating or cooling. They provide valuable insights into the thermal properties of substances, such as their melting and boiling points, specific heat capacities, and enthalpy changes.
The purpose of a heating and cooling curves worksheet is to guide students through the process of collecting and analyzing data from a heating or cooling experiment. By following the steps Artikeld in the worksheet, students can determine the thermal properties of the substance being studied.
Materials and Equipment
- Substance to be tested
- Thermometer
- Heating source (e.g., Bunsen burner, hot plate)
- Cooling source (e.g., ice bath, cold water)
- Insulated container
- Stopwatch or timer
- Graph paper or computer software for plotting data
Safety Precautions:Wear appropriate safety gear, such as gloves and eye protection, when working with heating and cooling equipment.
Procedure, Heating and cooling curves worksheet answers
- Measure the mass of the substance.
- Place the substance in an insulated container.
- Insert the thermometer into the substance.
- Heat the substance at a constant rate while recording the temperature at regular intervals.
- Continue heating until the substance reaches its boiling point.
- Remove the heat source and allow the substance to cool while recording the temperature at regular intervals.
- Continue cooling until the substance reaches room temperature.
Data Collection and Analysis
Plot the temperature data on a graph with temperature on the y-axis and time on the x-axis. The resulting graph is called a heating and cooling curve.
Analyze the curve to identify the following features:
- Melting point: The temperature at which the substance changes from a solid to a liquid.
- Boiling point: The temperature at which the substance changes from a liquid to a gas.
- Specific heat capacity: The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of the substance by 1 degree Celsius.
- Enthalpy changes: The heat absorbed or released during phase changes (e.g., melting, boiling).
Examples and Applications
Heating and cooling curves can be used to study the thermal properties of various substances, including metals, polymers, and biological materials.
Examples of applications include:
- Determining the purity of a substance
- Identifying unknown substances
- Optimizing industrial processes
- Understanding the behavior of materials in different environments
Tables and Diagrams
Table:Organize the data collected from the heating and cooling experiment in a table with the following columns: Time, Temperature, Phase.
Diagram:Draw a heating and cooling curve diagram to illustrate the changes in temperature over time. Label the different stages of the process (e.g., heating, melting, boiling, cooling).
Discussion and Interpretation
Discuss the significance of the data collected from the heating and cooling curve. Explain how the results can be interpreted to understand the thermal properties of the substance being studied.
Consider the following factors:
- The shape of the curve
- The temperature at which phase changes occur
- The specific heat capacity of the substance
FAQ Guide
What are heating and cooling curves?
Heating and cooling curves are graphical representations that depict the temperature changes of a substance as it undergoes heating or cooling processes.
What is the purpose of a heating and cooling curves worksheet?
Heating and cooling curves worksheets provide structured guidance for students to collect and analyze data related to the thermal behavior of substances.
How can I interpret heating and cooling curves?
By analyzing the shape, slopes, and plateaus of heating and cooling curves, you can identify phase transitions, calculate enthalpy changes, and determine the thermal properties of substances.