Draw the organic products formed in each reaction – Delving into the realm of organic product formation, this discourse explores the intricacies of chemical reactions that give rise to a diverse array of organic compounds. By unraveling the mechanisms and factors that govern product formation, we gain invaluable insights into the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, polymers, and other materials that shape our world.
Organic reactions, driven by the interplay of functional groups and reaction conditions, orchestrate the formation of countless organic products. Understanding the principles that underpin these reactions empowers chemists to predict and control the outcomes, paving the way for targeted synthesis and the development of novel materials with tailored properties.
1. Organic Products Formation
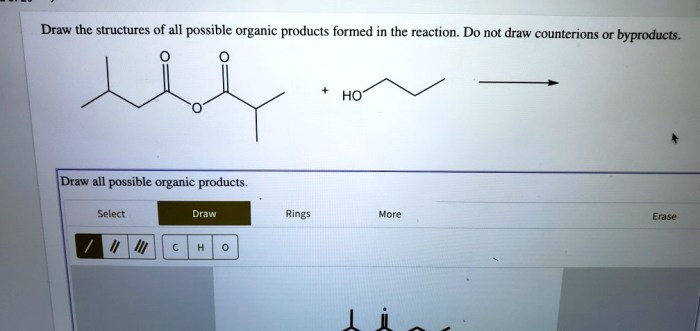
Organic product formation is a crucial aspect of chemical reactions involving organic compounds. These reactions lead to the creation of new organic molecules with specific structures and properties.
There are various types of organic reactions that can result in product formation, including:
- Addition reactions
- Elimination reactions
- Substitution reactions
- Rearrangement reactions
- Cyclization reactions
Each type of reaction involves different mechanisms and reactants, leading to distinct organic products.
2. Factors Influencing Product Formation
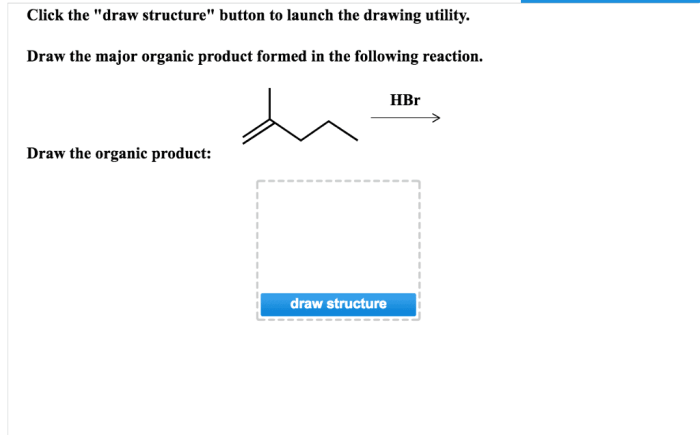
The formation of organic products is influenced by several factors, including:
Temperature
Temperature can affect the rate and selectivity of organic reactions. Higher temperatures generally favor reactions with lower activation energies and promote the formation of more stable products.
Pressure
Pressure can influence the equilibrium of reactions, particularly in gas-phase reactions. Increased pressure can shift the equilibrium towards the side with fewer moles of gas, which can affect product formation.
Catalysts
Catalysts are substances that enhance the rate of a reaction without being consumed. They can provide alternative reaction pathways with lower activation energies, leading to increased product formation.
Reaction Conditions
Reaction conditions such as solvent, pH, and reaction time can also influence product formation. These conditions can affect the stability of reactants and products, as well as the selectivity of the reaction.
3. Methods for Predicting Product Formation
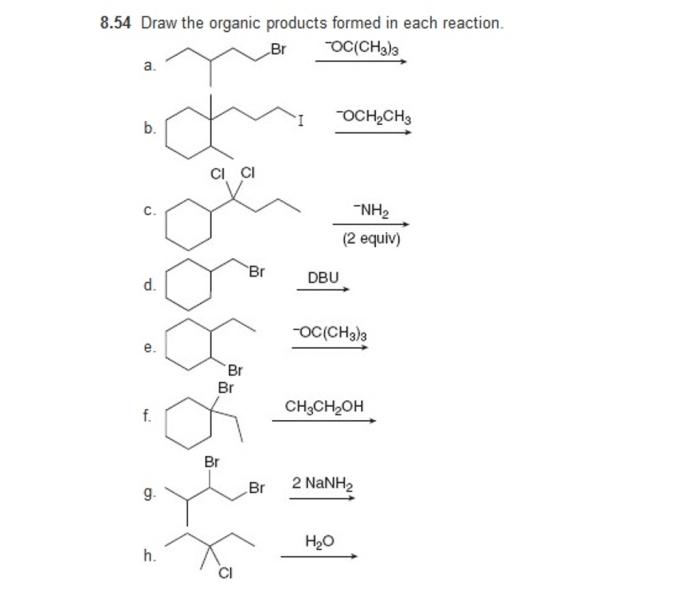
Predicting the products of organic reactions is essential for designing and optimizing synthetic strategies. Several methods are used for this purpose:
Reaction Mechanisms
Understanding the reaction mechanism provides insights into the steps involved in the formation of products. By analyzing the intermediates and transition states, chemists can predict the most likely products.
Energy Diagrams
Energy diagrams depict the energy changes during a reaction. They help identify the activation energies and reaction pathways, which can assist in predicting product formation.
Limitations and Challenges
Predicting product formation is not always straightforward. Factors such as complex reaction mechanisms, side reactions, and competing pathways can make it challenging to accurately predict the outcome of reactions.
4. Applications of Product Formation: Draw The Organic Products Formed In Each Reaction
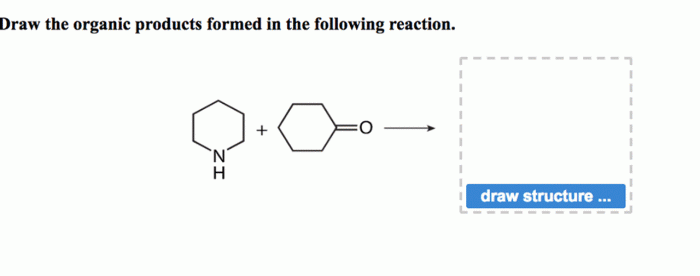
Organic product formation has wide-ranging applications in various fields:
Pharmaceuticals
Organic synthesis is crucial for the development of new pharmaceuticals. By designing and synthesizing specific organic molecules, researchers can create drugs with desired therapeutic properties.
Polymers
Organic reactions are used to produce polymers, which are essential materials in plastics, fibers, and other industries. The type of organic reaction used determines the structure and properties of the resulting polymer.
Chemical Engineering
Organic product formation is fundamental in chemical engineering processes, such as refining crude oil and producing chemicals on a large scale.
Environmental Chemistry, Draw the organic products formed in each reaction
Organic reactions play a role in environmental chemistry, such as the degradation of pollutants and the synthesis of environmentally friendly materials.
Essential Questionnaire
What factors influence the formation of organic products?
The formation of organic products is influenced by a multitude of factors, including temperature, pressure, reaction time, solvent effects, and the presence of catalysts.
How can we predict the products of organic reactions?
Predicting the products of organic reactions involves understanding reaction mechanisms and energy diagrams, which provide insights into the reaction pathways and the stability of intermediate and final products.
What are the applications of organic product formation?
Organic product formation finds applications in diverse fields, including the synthesis of pharmaceuticals, polymers, and other materials, as well as in chemical engineering and environmental chemistry.