Which practice requires a variance based on haccp – In the realm of food safety management, understanding which practices necessitate a variance based on HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) is crucial. This article delves into the concept of HACCP and variance, exploring the situations where variances are required, the procedures for obtaining them, their impact on HACCP plans, and the responsibilities involved in their management.
HACCP, a systematic approach to food safety, identifies and controls hazards throughout the food production process. Variances, on the other hand, are deviations from established HACCP plans that may be necessary under certain circumstances. Understanding when and how to apply variances is essential to ensure the continued effectiveness of HACCP systems.
Introduction to HACCP and Variance
HACCP (Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points) is a systematic approach to food safety management that focuses on identifying, assessing, and controlling hazards that could occur during food production, storage, and distribution. A variance is a deviation from the established HACCP plan that is necessary to maintain the safety of the food product.
Situations Requiring Variance
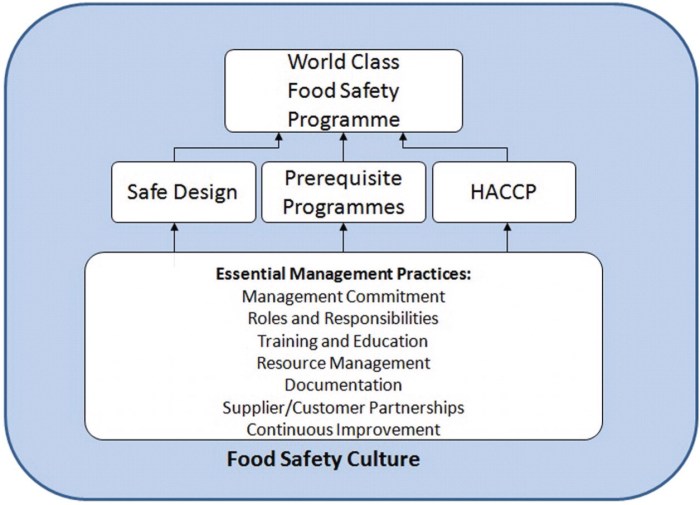
Variances are required in situations where it is necessary to deviate from the established HACCP plan to ensure the safety of the food product. Some examples of situations that may require a variance include:
- When new equipment or processes are introduced that require changes to the HACCP plan.
- When there is a temporary shortage of a critical ingredient or resource.
- When there is a need to make a change to the production process to improve efficiency or quality.
Procedures for Obtaining a Variance

The procedures for obtaining a variance vary depending on the specific situation and the requirements of the regulatory authority. However, in general, the following steps are involved:
- Identify the need for a variance and document the reasons for the deviation.
- Submit a request for a variance to the appropriate regulatory authority.
- Provide documentation and evidence to support the request for a variance.
- Obtain approval from the regulatory authority for the variance.
Impact of Variance on HACCP Plan

Variances can have a significant impact on the overall HACCP plan. It is important to ensure that variances are managed effectively to maintain the safety of the food product. Some of the potential impacts of variances include:
- Changes to the critical control points (CCPs) or critical limits (CLs).
- Changes to the monitoring procedures.
- Changes to the corrective actions.
- Changes to the verification procedures.
Responsibilities and Accountability
The responsibility for managing variances lies with the food safety team. The team should develop procedures for obtaining, reviewing, and approving variances. The team should also be responsible for ensuring that variances are implemented and monitored effectively.
Examples and Case Studies: Which Practice Requires A Variance Based On Haccp
There are many examples of variances that have been granted in the food industry. Some examples include:
- A variance to allow the use of a different type of packaging material.
- A variance to allow the use of a different type of cleaning agent.
- A variance to allow the use of a different type of equipment.
Detailed FAQs
What is the purpose of a variance in HACCP?
Variances allow for temporary deviations from established HACCP plans when necessary to address unforeseen circumstances or process changes.
Who is responsible for approving variances?
The HACCP team, in consultation with relevant stakeholders, is typically responsible for approving variances.
What documentation is required for a variance?
Variances should be documented in writing, including the reason for the variance, the duration, and any corrective actions taken.