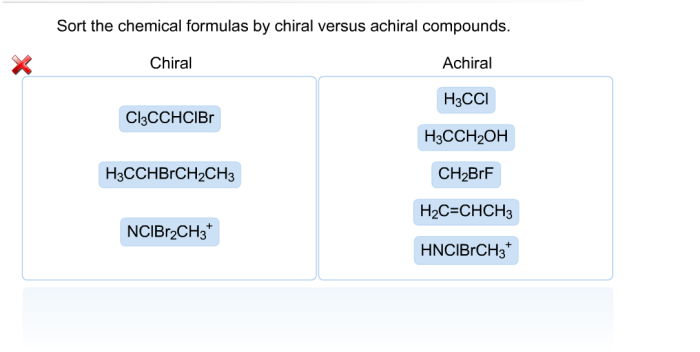
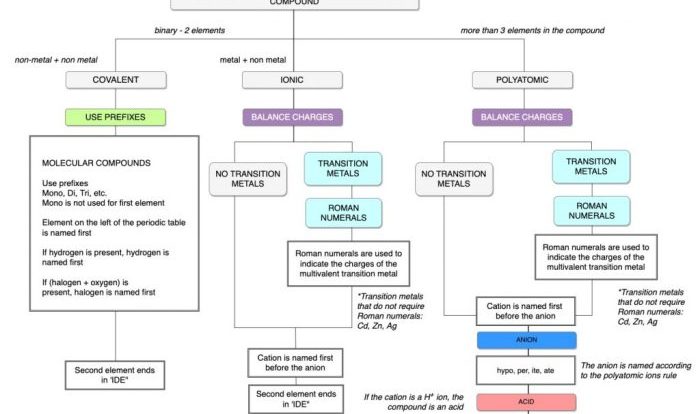
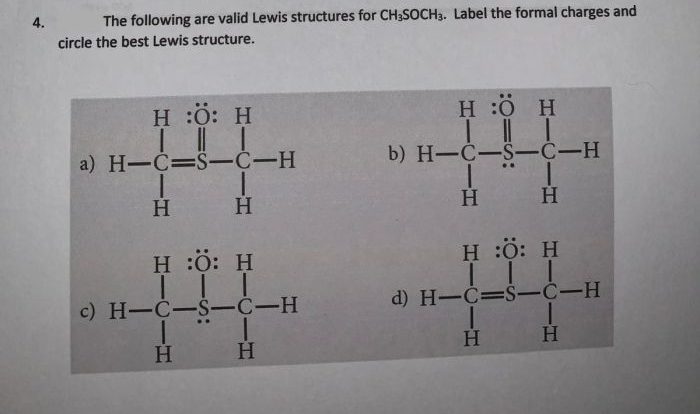
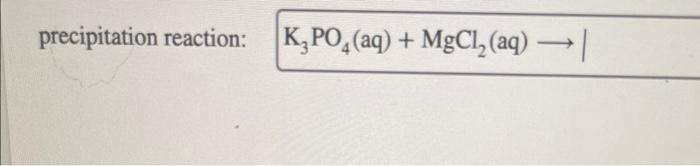Select all of the true statements regarding chemical equilibrium. Chemical equilibrium is a fundamental concept in chemistry that describes the state of a system in which the concentrations of the reactants and products do not change over time. This dynamic state is the result of the forward and reverse reactions occurring at the same rate, leading to a constant composition of the system.
Chemical equilibrium is characterized by several key features. The concentrations of the reactants and products remain constant, and there is no net change in the composition of the system. The reactions are reversible, meaning that the products can react to form the reactants, and vice versa.
The position of equilibrium, or the relative amounts of reactants and products, can be shifted by changing the conditions of the system, such as temperature, pressure, or concentration.
Definition of Chemical Equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium is a dynamic state in which the concentrations of the reactants and products of a chemical reaction remain constant over time. It is a result of the forward and reverse reactions occurring at the same rate, with no net change in the concentrations of the reactants and products.
At equilibrium, the system is in a state of balance, where the opposing forces of the forward and reverse reactions are equal. This does not mean that the reaction has stopped, but rather that the rates of the forward and reverse reactions are equal, resulting in no net change in the concentrations of the reactants and products.
Characteristics of Chemical Equilibrium
- Constant concentrations of reactants and products
- No net change in the concentrations of reactants and products
- Dynamic state, with forward and reverse reactions occurring at the same rate
- Reversible reactions, where the products can react to form the reactants
Factors Affecting Chemical Equilibrium
The position of equilibrium can be shifted by changing certain factors, such as:
- Concentration of reactants and products
- Temperature
- Pressure (for gas-phase reactions)
These factors can be used to control the equilibrium position and favor the formation of desired products.
Applications of Chemical Equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium has numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Industrial processes, such as the Haber process for ammonia production
- Environmental chemistry, such as understanding the behavior of pollutants in the atmosphere
- Biological systems, such as the regulation of pH in the body
Understanding chemical equilibrium is crucial for optimizing these processes and predicting the behavior of chemical systems.
Mathematical Representation of Chemical Equilibrium, Select all of the true statements regarding chemical equilibrium.
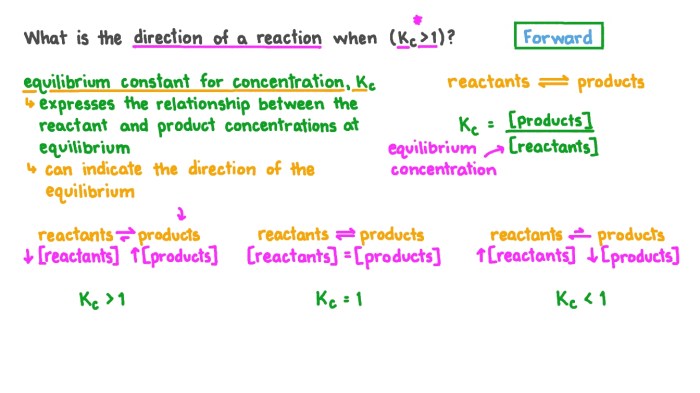
The equilibrium constant (Kc or Kp) is a mathematical expression that represents the equilibrium position of a reaction. It is calculated using the concentrations of the reactants and products at equilibrium.
| Equilibrium Constant | Expression |
|---|---|
| Kc (concentration equilibrium constant) | Kc = [products]/[reactants] |
| Kp (pressure equilibrium constant) | Kp = (partial pressure of products)/(partial pressure of reactants) |
The equilibrium constant is a constant for a given reaction at a specific temperature. It can be used to calculate the equilibrium concentrations of the reactants and products.
Types of Chemical Equilibrium
- Homogeneous equilibrium: Reactions that occur in a single phase, such as a gas or liquid phase
- Heterogeneous equilibrium: Reactions that occur between different phases, such as a solid and a gas phase
- Gas-phase equilibrium: Reactions that occur between gases
Each type of equilibrium has its own characteristics and applications.
Limitations of Chemical Equilibrium
Chemical equilibrium theory assumes that the reaction is at constant temperature and pressure, and that the reactants and products are ideal gases or solutions. In reality, these assumptions may not always be valid.
Additionally, chemical equilibrium theory does not take into account reaction kinetics, which can affect the rate at which equilibrium is established.
Essential FAQs: Select All Of The True Statements Regarding Chemical Equilibrium.
What is chemical equilibrium?
Chemical equilibrium is a state in which the concentrations of the reactants and products do not change over time.
What are the characteristics of chemical equilibrium?
The characteristics of chemical equilibrium include constant concentrations, no net change in composition, and reversibility of reactions.
What factors can shift the equilibrium position?
The equilibrium position can be shifted by changing the temperature, pressure, or concentration of the system.
What are the applications of chemical equilibrium?
Chemical equilibrium has applications in various fields, including industrial processes, environmental chemistry, and biochemistry.
What are the limitations of chemical equilibrium theory?
Chemical equilibrium theory has limitations, such as the assumption of ideal behavior and the neglect of reaction kinetics.